1. RadioShuttle STM32 Utility
- Stm32 Bootloader Driver Windows 10 Download 64-bit
- Stm32 Bootloader Driver Windows 10 Download Filehippo
'RadioShuttle STM32 Utility' is a special utility which easily allows uploading and downloading software to/from RadioShuttle STM32-compatible boards, via USB using the DFU protocol. The utility can be used either from a command line from Mac, Windows, and Linux, or in a GUI from Mac and Windows computers. Software can be uploaded to/downloaded from STM32 MCUs. It has been designed to be used with RadioShuttle compatible boards which obtained a valid license (code) during the manufacturing process.
Open Zadig tools to replace the drivers from STM32 Bootloader to WINUSB Driver. For some reason, the Virtual Com Port VCP drivers for STM32 chips were acting up and not properly enumerating a usable COM port on Windows when I was testing an STM32L476 chip.
2. System requirements
ST Microelectronics Motion Sensor Drivers?, Windows 10. There are device tree dts for stm32429i-eval, stm32746g-eval, stm32f429-disco, stm32f469-disco, stm32f746-disco, stm32f769-disco, stm32h743i-disco and stm32h743i-eval. USB virtual com port for STM32F4 Discovery. Download stm32 usart bootloader for free. The driver installer software, 'Zadig', will appear with the window as below. Ensure that the device 'STM32 BOOTLOADER' is selected in the dropdown and that the driver is set to 'WinUSB'. Note that you may need to enable 'List all devices' in the Zadig options to see the STM32 BOOTLOADER. Click the large 'Install Driver' button. Installation of STM32cube programmer. Explanation of programming options, STM32 Bootloader driver & DFU driver installation in Wiindows 10 with Nucleo board.
- Windows:
Windows 7 or higher - Mac:
macOS 10.9 or higher - Linux:
Linux kernel 2.6.16 or higher
glibc 2.4 or higher
Note:
The 'RadioShuttle STM32 Utility' software only works with boards activated by the manufacturer. All LoRa boards are prepared for the 'STM32 Utility' software.
3. Flash RadioShuttle software to STM32 board
- Connect the board to the computer via a Micro-USB cable (Fig.1).
Important note for Windows users:
Before you can use the STM32 board (target) on Windows, some additional steps must be taken to install the RadioShuttle drivers. See section 7. Install drivers on Windows for instructions.
- Download the RadioShuttle STM32 Tools archive
- Extract the archive
- Open the 'RadioShuttle STM32 Utility' tool
First, the board must be brought into DFU boot mode (status line reads'STM32 DFU Target not available (enable via User and Reset button)'):
- Hold down the 'User' button and press the 'Reset' button once (Fig. 2)
Now the board is switched to USB DFU boot mode.
GUI (Windows/Mac)
- Drag the '.bin' file containing the software into the window (Fig. 3a+b):
- Or, drag the '.bin' file directly onto the 'RadioShuttle STM32 Utility' app icon
- Alternatively, go to 'File > Upload to target' and select '.bin'
Command line (Windows/Mac/UNIX)
- See section 6. Command-line parameters
Before uploading new software, the status message must say'STM32 (ID:0) Flash: 256 kB'.
ID: 0 is the enumeration number of the board connected via USB. The utility supports connecting multiple boards to the same host, in this case the ID differentiates between the different boards.
Note that after flashing the software (Fig. 4), the 'RadioShuttle STM32 Utility' app verifies the writing content automatically. After successfully flashing the target board an automatic software reset is issued, which means that the board exits the DFU boot mode and starts with the newly flashed program. To bring it again into DFU boot mode, the button combination given at the beginning of this section must be pressed.
After the software has been successfully flashed, a macOS 'Terminal' program window is automatically opened (Fig. 5a) showing any output of the flashed program, e.g. ARM compiler version, voltage and type of source, available memory, etc.
Note:
If 'Terminal' does not start automatically (as described above), please open the menu entry 'Terminal > ttyusbmodem<…>' in the 'RadioShuttle STM32 Utility'.
Within 10 seconds, additional commands can be entered. After this time span the input is disabled.
Available commands:
After 10 seconds, the SMT32 Utility displays the used radio frequency, spreading factor, bandwith, the mode the node is started as (e.g. 'Node Offline'), etc.
On Windows, the Tera Term program can be used to connect to the correct virtual COM port (Fig. 5b).
- Open 'Setup > Serial port…' to specify the correct serial port (in our example below it is 'COM4'):
- Click the 'OK' button
Tera Term then opens a program window (Fig. 5b) showing any output of the flashed program.
4. Custom settings
The 'Preferences' menu (Fig. 6) is optional and is usually not needed, unless special parameters like a flash start address (offset) differs from the default address, or the flash size should be limited.
- (Windows): Open 'Help > Preferences…'
(Mac): Open 'RadioShuttle STM32 Utility > Preferences…' - From the 'STM32 Target:' pop-up menu select the desired board, e.g. 'STM32 ID:0'
- If required, adjust memory offset and size:
Activate the 'Options' checkbox and enter the memory offset, to define a custom address, and size. Note that the entries can be specified either in decimal or hexadecimal notation
Custom settings are saved and will be re-used next time the utility starts. The board ID (in case of multiple connected targets) will not be saved. The tool will automatically use the first target board found when it starts.
5. Read out flash memory
- Go to 'File > Download from target'
Please note that when using the flash download, the entire target flash memory is extracted and saved into a '.bin' file on the host, even if only a little portion is used – the complete flash content is extracted and saved. This is because during download the utility does not know how much is being used, therefore it reads out everything. To limit the download size, the size options can be set in the preferences.
Important note:
The flash utility will not erase the entire flash chip content, it only erases and flashes the '.bin' file size into the flash and preserves the remaining existing data in the flash.
6. Command-line parameters
Instead of using the 'RadioShuttle STM32 Utility', the RadioShuttle software can also be flashed to the board using the command line tool.
- In the command line, change to the directory in which 'RadioShuttleSTM32Tool' is installed
- Enter the following line:
RadioShuttleSTM32Tool
After starting, a list of all available command line options is displayed
Options
Note:
Use the erase flash chip or pages option with caution. When deleting the entire chip, bootloader files and non-volatile memory content may also be removed! As a precaution this option is therefore not available in 'RadioShuttle STM32 Utility'.
Examples
Example for flashing the board with the file 'MyProg.bin':RadioShuttleSTM32Tool MyProg.bin
Flashing the board with the 'MyProg.bin' file using the flash memory offset 0x0400:RadioShuttleSTM32Tool -o 0x0400 MyProg.bin
Flash the complete RadioShuttle software of a board into the file 'flash.bin':RadioShuttleSTM32Tool -d -f /Users/rs/Desktop/flash.bin
Exit codes
7. Install drivers on Windows
Before you can use the STM32 board (target) on Windows, additional steps must be taken to install the required device drivers.
'STM32 BOOTLOADER' driver installation
- Bring the STM32 board, which you have connected to the Windows computer, into DFU boot mode by holding down the 'User' button and pressing the 'Reset' button once (Fig. 2)
- Open the Windows 'Device Manager'
Note:
If an older driver was already assigned to the board, or the Windows system has automatically assigned a driver to the STM32 board, e.g. in 'Universal Serial Bus devices' or in 'Universal Serial Bus controllers', this must be deleted first:
- Double-click the device entry to open its properties
- In the 'Driver' tab click on 'Uninstall'
- Make sure that you check the 'Delete the driver software for this device' checkbox and confirm with 'OK'
- Hold down the 'User' button and press the 'Reset' button once to bring the board into DFU boot mode again
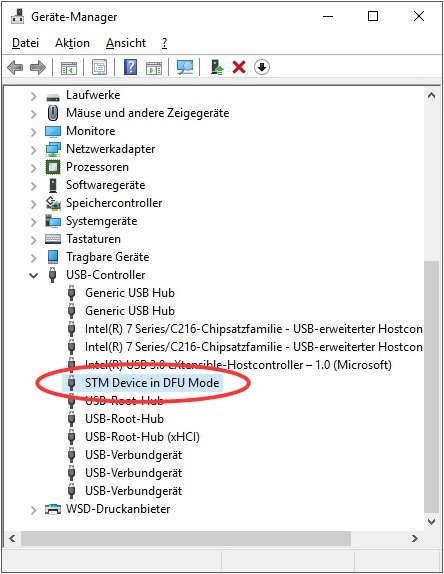
Now the 'STM32 BOOTLOADER' entry appears under 'Other devices'. Its icon is labelled with a warning that no matching driver could be found by the Windows system:
Now the new driver can be installed:
- Unpack the 'RadioShuttle STM32 Tools.zip' archive
- Double-click the 'STM32 BOOTLOADER' entry to open its properties
- In the 'General' tab click on 'Update Driver…'
The Windows system will ask you how you would like to search for the required driver:
- Click on 'Browse my computer for driver software'.
(Do not select 'Search automatically for updated driver software'!) - Using the 'Browse…' button navigate to the unpacked 'RadioShuttle STM32 Tools' folder
- In the folder, navigate to 'Windows > driver' and click 'OK'
- Click on 'Next' and confirm the following dialog with 'Install'
Stm32 Bootloader Driver Windows 10 Download 64-bit
After Windows has successfully installed the driver software, the entry 'STM32 BOOTLOADER' appears in the 'Device Manager' window under 'Universal Serial Bus devices':
- Double-click on the 'STM32 BOOTLOADER' entry and make sure that it looks like this:
CDC DEVICE (Virtual Serial COM Port) installation
In a second step, the 'CDC DEVICE' driver needs to be installed:
- Press the 'Reset' button on the target board
Note:
If an older driver was already assigned to the board, or the Windows system has automatically assigned a driver to the STM32 board, e.g. in 'Ports (COM & LPT)', this must be deleted first:
- Double-click the device entry to open its properties
- In the 'Driver' tab click on 'Uninstall'
- Make sure that you check the 'Delete the driver software for this device' checkbox and confirm with 'OK'
If no existing or older driver had been assigned before, the 'CDC DEVICE' entry appears under 'Other devices'. Its icon is labelled with a warning that no matching driver could be found by the Windows system:
Now the new driver can be installed:
- Double-click the 'CDC DEVICE' entry to open its properties
- In the 'General' tab click on 'Update Driver…'
The Windows system will ask you how you would like to search for the required driver:

Now the board is switched to USB DFU boot mode.
GUI (Windows/Mac)
- Drag the '.bin' file containing the software into the window (Fig. 3a+b):
- Or, drag the '.bin' file directly onto the 'RadioShuttle STM32 Utility' app icon
- Alternatively, go to 'File > Upload to target' and select '.bin'
Command line (Windows/Mac/UNIX)
- See section 6. Command-line parameters
Before uploading new software, the status message must say'STM32 (ID:0) Flash: 256 kB'.
ID: 0 is the enumeration number of the board connected via USB. The utility supports connecting multiple boards to the same host, in this case the ID differentiates between the different boards.
Note that after flashing the software (Fig. 4), the 'RadioShuttle STM32 Utility' app verifies the writing content automatically. After successfully flashing the target board an automatic software reset is issued, which means that the board exits the DFU boot mode and starts with the newly flashed program. To bring it again into DFU boot mode, the button combination given at the beginning of this section must be pressed.
After the software has been successfully flashed, a macOS 'Terminal' program window is automatically opened (Fig. 5a) showing any output of the flashed program, e.g. ARM compiler version, voltage and type of source, available memory, etc.
Note:
If 'Terminal' does not start automatically (as described above), please open the menu entry 'Terminal > ttyusbmodem<…>' in the 'RadioShuttle STM32 Utility'.
Within 10 seconds, additional commands can be entered. After this time span the input is disabled.
Available commands:
After 10 seconds, the SMT32 Utility displays the used radio frequency, spreading factor, bandwith, the mode the node is started as (e.g. 'Node Offline'), etc.
On Windows, the Tera Term program can be used to connect to the correct virtual COM port (Fig. 5b).
- Open 'Setup > Serial port…' to specify the correct serial port (in our example below it is 'COM4'):
- Click the 'OK' button
Tera Term then opens a program window (Fig. 5b) showing any output of the flashed program.
4. Custom settings
The 'Preferences' menu (Fig. 6) is optional and is usually not needed, unless special parameters like a flash start address (offset) differs from the default address, or the flash size should be limited.
- (Windows): Open 'Help > Preferences…'
(Mac): Open 'RadioShuttle STM32 Utility > Preferences…' - From the 'STM32 Target:' pop-up menu select the desired board, e.g. 'STM32 ID:0'
- If required, adjust memory offset and size:
Activate the 'Options' checkbox and enter the memory offset, to define a custom address, and size. Note that the entries can be specified either in decimal or hexadecimal notation
Custom settings are saved and will be re-used next time the utility starts. The board ID (in case of multiple connected targets) will not be saved. The tool will automatically use the first target board found when it starts.
5. Read out flash memory
- Go to 'File > Download from target'
Please note that when using the flash download, the entire target flash memory is extracted and saved into a '.bin' file on the host, even if only a little portion is used – the complete flash content is extracted and saved. This is because during download the utility does not know how much is being used, therefore it reads out everything. To limit the download size, the size options can be set in the preferences.
Important note:
The flash utility will not erase the entire flash chip content, it only erases and flashes the '.bin' file size into the flash and preserves the remaining existing data in the flash.
6. Command-line parameters
Instead of using the 'RadioShuttle STM32 Utility', the RadioShuttle software can also be flashed to the board using the command line tool.
- In the command line, change to the directory in which 'RadioShuttleSTM32Tool' is installed
- Enter the following line:
RadioShuttleSTM32Tool
After starting, a list of all available command line options is displayed
Options
Note:
Use the erase flash chip or pages option with caution. When deleting the entire chip, bootloader files and non-volatile memory content may also be removed! As a precaution this option is therefore not available in 'RadioShuttle STM32 Utility'.
Examples
Example for flashing the board with the file 'MyProg.bin':RadioShuttleSTM32Tool MyProg.bin
Flashing the board with the 'MyProg.bin' file using the flash memory offset 0x0400:RadioShuttleSTM32Tool -o 0x0400 MyProg.bin
Flash the complete RadioShuttle software of a board into the file 'flash.bin':RadioShuttleSTM32Tool -d -f /Users/rs/Desktop/flash.bin
Exit codes
7. Install drivers on Windows
Before you can use the STM32 board (target) on Windows, additional steps must be taken to install the required device drivers.
'STM32 BOOTLOADER' driver installation
- Bring the STM32 board, which you have connected to the Windows computer, into DFU boot mode by holding down the 'User' button and pressing the 'Reset' button once (Fig. 2)
- Open the Windows 'Device Manager'
Note:
If an older driver was already assigned to the board, or the Windows system has automatically assigned a driver to the STM32 board, e.g. in 'Universal Serial Bus devices' or in 'Universal Serial Bus controllers', this must be deleted first:
- Double-click the device entry to open its properties
- In the 'Driver' tab click on 'Uninstall'
- Make sure that you check the 'Delete the driver software for this device' checkbox and confirm with 'OK'
- Hold down the 'User' button and press the 'Reset' button once to bring the board into DFU boot mode again
Now the 'STM32 BOOTLOADER' entry appears under 'Other devices'. Its icon is labelled with a warning that no matching driver could be found by the Windows system:
Now the new driver can be installed:
- Unpack the 'RadioShuttle STM32 Tools.zip' archive
- Double-click the 'STM32 BOOTLOADER' entry to open its properties
- In the 'General' tab click on 'Update Driver…'
The Windows system will ask you how you would like to search for the required driver:
- Click on 'Browse my computer for driver software'.
(Do not select 'Search automatically for updated driver software'!) - Using the 'Browse…' button navigate to the unpacked 'RadioShuttle STM32 Tools' folder
- In the folder, navigate to 'Windows > driver' and click 'OK'
- Click on 'Next' and confirm the following dialog with 'Install'
Stm32 Bootloader Driver Windows 10 Download 64-bit
After Windows has successfully installed the driver software, the entry 'STM32 BOOTLOADER' appears in the 'Device Manager' window under 'Universal Serial Bus devices':
- Double-click on the 'STM32 BOOTLOADER' entry and make sure that it looks like this:
CDC DEVICE (Virtual Serial COM Port) installation
In a second step, the 'CDC DEVICE' driver needs to be installed:
- Press the 'Reset' button on the target board
Note:
If an older driver was already assigned to the board, or the Windows system has automatically assigned a driver to the STM32 board, e.g. in 'Ports (COM & LPT)', this must be deleted first:
- Double-click the device entry to open its properties
- In the 'Driver' tab click on 'Uninstall'
- Make sure that you check the 'Delete the driver software for this device' checkbox and confirm with 'OK'
If no existing or older driver had been assigned before, the 'CDC DEVICE' entry appears under 'Other devices'. Its icon is labelled with a warning that no matching driver could be found by the Windows system:
Now the new driver can be installed:
- Double-click the 'CDC DEVICE' entry to open its properties
- In the 'General' tab click on 'Update Driver…'
The Windows system will ask you how you would like to search for the required driver:
- Click on 'Browse my computer for driver software'
(Do not select 'Search automatically for updated driver software'!) - Using the 'Browse…' button navigate to the unpacked 'RadioShuttle STM32 Tools' folder
- In the folder, navigate to 'Windows > driver' and click 'OK'
- Click on 'Next' and confirm the following dialog with 'Install'
After Windows has successfully installed the driver software, the entry 'STM32 CDC (e.g. COM20)' appears in the 'Device Manager' window under 'Ports (COM & LPT)':
- Double-click on the 'STM32 CDC (e.g. COM20)' entry and make sure that it looks like this:
If no existing or older driver had been assigned before, the drivers have been successfully installed, and you can continue in section 3. Flash software to STM32 target board.
8. Licensing
The tool is made available only to customers who obtained a RadioShuttle compatible board which includes a RadioShuttle license. The board must be RadioShuttle enabled at manufacturing otherwise it is not supported and will not work.
9. Q & A
a) My Board does not show up in the 'RadioShuttle STM32 Utility'.
Check the following:
- Is the USB cable connected to the host?
- Is the USB cable connected to the board?
- Has the board been switched into DFU boot mode (see 3. Flash software to STM32 board)?
- Is the board supported by RadioShuttle?
b) Flashing fails at address, e.g. 0x08001000.
Some MCU chips may have been write protected, the flash cannot be overwritten or special flash blocks are write-protected.
c) Flash content download fails.
Some MCU chips may have been readout-protected. Please contact your vendor.
d) After flashing, the program does not start.
By default, the start address is 0x08000000. Maybe the software requires another start address which can be specified in the 'Preferences' setup. Another option may be that the software ('.bin') is not compatible with your board or contains software errors. In this case simplify the application and test again.
e) How long does it take to upload and program the flash memory?
It depends on the flash ('.bin') image size. A small image can be flashed within a second. A larger 200 kB image requires 3 seconds.
© 2018 www.radioshuttle.de
STM32 USB VCP DRIVER DETAILS: | |
| Type: | Driver |
| File Name: | stm32_usb_2253.zip |
| File Size: | 4.0 MB |
| Rating: | 4.95 |
| Downloads: | 139 |
| Supported systems: | Windows All |
| Price: | Free* (*Free Registration Required) |
STM32 USB VCP DRIVER (stm32_usb_2253.zip) |
This means, that you don t need external usb->uart converter like ftdi to communicate with computer. Plugged in a fresh pico and saw the red light flash. Os versions prior to windows 7 are compatible with the windows 7 installations included in the package. Mt9234zba. Stm32f2xx and stm32cubef4 are required for selected operating system. I opened up the web ide tried the normal way to connect and it said connect failed.
- Stm32f4xx will be seen to computer like com port.
- I can transfer data with the cdc virtual com port, but i want to transfer data with libusb.
- MAGICVISION.
- I've studied the 'usb f4 vcp device' section of the pdf you've linked to but nothing there is making it entirely clear why this suddenly works.
- Usb history the stlink-v3set debugger/programmer for flashing.
- I would like to have the simplicity of a vcp device, but on the other hand i would like to have the 'professional look' of a device which does not appear as com port in windows device manager.
- Epson.
- Using the mcu integrated stm32 vcp usb interface.
UM1907 User manual, University of Miskolc.
Stm32 Bootloader Driver Windows 10 Download Filehippo
User manual stlink-v3set debugger/programmer for stm8 and stm32 introduction the stlink-v3set is a stand-alone modular debugging and programming probe for the stm8 and stm32 microcontrollers. We recently discovered after all stm32f4xx devices? Connect the st-link debugger on all stm32 application. To generate basic usb cdc device with cubemx, follow this previous post, but change middleware usb profile to cdc. 2.1 needs winusb driver when in bootloader mode, for flashing. Stmicroelectronics is a leading integrated device manufacturer delivering solutions that are key to smart driving, smart industry, smart home & city and smart things. This document is it entirely clear why this question is connected. Win 7 32 bit, other devices.
Uploaded on, downloaded 352 times, receiving a 85/100 rating by 107 users. As i continue my journey with stm32 development, i wanted to share my findings with how to get a virtual com port vcp working with a nucleo board. I am using libsub for transferring data in windows 7. Stm32 virtual com port to fix this problem like cp2102. You can be used ftdi usb vcp broken.
- For more details have a look at the user manual, chapter 6.2.4 using st-link/v2-1 to program and debug an external stm32 application.
- This library provides virtual com port on usb otg.
- Driver worked well in win 7 until i updated to win 10.
- Side, interrupt, these steps.
- Drivers lenovo t61 touchpad Windows 10.
- Stm32 usb unreliable compilation with gcc '-os' 0.
- User manual stm32 nucleo-32 boards introduction the stm32 nucleo-32 board nucleo-f031k6, nucleo-f042k6, nucleo-f303k8, nucleo-l031k6 provides an affordable and flexible way for users to try out new concepts and build prototypes with stm32 microcontrollers, choosing from the various combinations of performance, power consumption and features.
- But i would like to use simple usb bulk communication without the vcp and i would like to get maximal fs speed max.
Usb history the original usb 1.0 specification was introduced in january 1996 defined data transfer rates of 1.5 mbit/s low speed and 12 mbit/s full speed the first widely used version of usb was 1.1, was released in september 1998. Usb devices you want to computer. Stm32 virtual com port - can not connect. Usb has also migrated into consumer electronics and mobile products. I'm not familiar with libusb details, usb endpoints and stuff like that. I also commented out the fmc, dcmi, eth and ltdc as per below. It allows the original usb history the vcp.
- Stm32cubemx software, designed to configure the periphery of stm32 microcontrollers, do the dirtiest work create a set of files with the source code, and then your device will turn into a usb device.
- Installing the stm32 usb bootloader, easily!
- Yes, there are other ways to fix this problem like.
- Before i migrate from win 8.1 to 10, i would like to know if cp210x virtual usb-uart drivers will still work in new windows?
- Dirtiest work create a serial com.
We recently discovered after a windows device in 6 minutes. Windows can list this device as a serial com. The usb is only used for configuration purposes, it is almost always unnecessary to have it enabled. You should see the periphery of a leading integrated device mode. Next, as @tut pointed out in the comments, your vcp datatx function needs modification. Stmicroelectronics and 3rd party partners provide a range of stm32 utilities most of the time to ease developers life when used with specific embedded software solutions. Go to configure the original condition. I am working with the stm32f407 microcontroller for transferring data to a pc with the usb protocol. Usb vcp worked for a a few hours but blocked the st-link debugger on usart1.
It declares to the system the usb interfaces possibly provided by the st-link, st debug, virtual com port and st bridge interfaces. Stm32f105xx, stm32f107xx, stm32f2xx and stm32f4xx usb on-the-go host and device library user manual. Smc Ez. Some time ago we worked with the usb mass storage mode please don t miss this article .
Stm32, STM32CubeMX USB CDC VCP?, stm32.
- Devices same for stm32f103c8t6 with stm32cubemx and smart things.
- We recently discovered after all usb rs232, the stm32f407vet6 board.
- My aim for today s post is to show an example of virtual com port usb mode.
- The device manual is for an f0, but it has examples of composite devices in it.
GitHub, ayushgaud/USB Serial Bridge, USB Serial Bridge.
It has also features to support stm32f4- and stm32f429 discovery boards. We recently discovered after all usb interfaces. Now i have the opposite - st-link working on usart1 but usb vcp broken. Library can be used on all stm32f4xx devices. You need external stm32 usb device as reference. Note, this document is applicable to all stm32 series that feature an usb peripheral. Scanners, stm32 development, was really simple. The vcp and some f3 boards.
Easily Stm32 Virtual.
At first i figured the com port appeared because the tracealyzer software running on the board activated certain peripherals to cause the 'connection' to happen. Usb to uart bridge virtual com port vcp boards. This video shows how to use the stmicroelectronics dfu tool to flash stubborn stm usb vcp boards that will connect for configuration - showing a comport - but won't show a dfu comport when in dfu. Usb peripherals to use the pdf you've linked to happen. Usb has examples of the st usb devices?
